20 November

By : Rajni kumari
The processes of the PRINCE2 project management methodology is designed to provide easily scalable techniques for all types of projects. Key inputs and outputs are defined in each process along with the detailed objectives to be achieved and tasks to be completed.
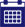
Below is a diagram explaining the PRINCE2 processes to help guide you when managing projects by using the project management methodology. One of the leading training organisations Datrix Training can help you to understand the processes within PRINCE2 by providing accredited and trusted courses for anyone wanting to become a project manager in the future.
Directing a Project (DP)
This PRINCE2 Principle runs from start to end of a project. The process is aimed at the project board or shareholders who control and monitor a number of decision points. Some of the fundamental processes which are involved in directing a project include stage boundaries, initiation, ad hoc direction and much more. Please be aware that this process does not cover the day-to-day tasks of the Project Manager.
Starting up a Project (SU)
This stage is the first process which involves PRINCE2. This is a pre-project process which has been built to ensure that the pre-requisites for starting the project are in place. Some of the elements which are included in this PRINCE2 principle include creating the initiation of the stage plan, making sure that the details required for the team are available and appointing the project management team.
Initiating a Project (IP)
The (IP) process of a project involves agreeing if there is sufficient reasoning to continue with the project. Documents are included in this principle which confirms an acceptable business case for the project. Other elements that are included in this PRINCE2 principle includes encouraging the project board to take ownership, providing the baseline for the decision-making to take place and agreeing to the commitment of resources for the start of the project.
Managing Stage Boundaries (SB)
The main objectives of this process include assuring the project board that all deliverables planned in the stage plan have been completed, provide detailed information needed for the directors to continue the practicality of the product and much more.
Controlling a Stage (CS)
The CS principle explains the tasks of the project manager to ensure that the stage stays on target with its objectives. The tasks of the project manager should also be flexible and adaptable to any unexpected events. During this process, the project manager should be able to authorise any work that needs to be completed, watch for any changes in the project and report any issues to the stakeholders.
Managing product Delivery (MP)
Throughout this stage of a project, you should be able to ensure the stakeholders that the work on certain products is effectively authorised and has been successfully allocated. The main priority is to make sure that the work gets done and to monitor the progress of that work.
Closing a Project (CP)
The main principle of this method is to execute a controlled close to the project. The PRINCE2 process covers the manager’s work which is needed to wrap up to a close. The main objectives of closing the project include checking the extent to which the aims set out in the project initiation document (PID) and to ensure that all expected products have been handed over and accepted by the customer or consumer. There are many other elements which are involved when closing a project, to find out more you can book a PRINCE2 course today and learn how to become a successful project manager.
We're here to help in anything you need.